The Impact of Food on Mental Health and Well-being
Food Choices Affect Mental Health
What you eat has a profound impact on your mental well-being. A healthy diet enriches gut flora, which produces neurotransmitters like serotonin that regulate mood.
For instance, consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. On the contrary, processed sugars can lead to mood swings and increased anxiety levels.
Nutrient-Dense Foods Enhance Cognitive Function
Staying hydrated and incorporating nutrient-dense foods into your diet can improve cognitive function.
Leafy greens and blueberries are examples of nutrient-dense foods that support brain health. By making informed choices about your meals, you can strengthen your emotional resilience and overall mental health.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection plays a crucial role in overall mental health.
The state of your digestive system can influence your mood and cognitive functions. This connection is possible because the gut isn't just a digesting organ, but a complex ecosystem of bacteria that communicates with the brain.
A balanced gut flora produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which is vital for regulating mood.
When the gut health deteriorates due to poor diet, stress, or other factors, it can lead to symptoms like anxiety or depression.
The gut microbiome sends signals to the brain, affecting how you feel and think. This connection explains why digestive issues often accompany mental health struggles.
Inflammation in the gut can lead to increased permeability, sometimes referred to as "leaky gut." This allows toxins to enter the bloodstream and potentially impact brain function.
Prioritizing gut health through nutrition and lifestyle choices can cultivate a more positive mental state. Understanding this connection empowers you to take proactive steps toward improving not just your digestive health, but also your emotional well-being.
Nutrients That Boost Mood
Nutrients That Boost Mood
Gut Health and Mood
Maintaining a healthy gut directly influences your mood and mental well-being.
A healthy gut produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, which regulates mood. Certain nutrients, such as B vitamins, play a crucial role in this process.
B Vitamins and Mood
B vitamins, especially B6, B12, and folate, produce neurotransmitters like serotonin. Foods rich in these vitamins, such as leafy greens, eggs, and legumes, can help boost your emotional health.
Complex Carbohydrates and Mood
Complex carbohydrates like whole grains stabilize blood sugar levels, providing a steady supply of energy and preventing mood swings. This helps maintain emotional balance throughout the day.
Magnesium and Anxiety
Magnesium, found in nuts, seeds, and dark chocolate, helps combat anxiety and promotes relaxation. Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet can reduce feelings of anxiety and stress.
Antioxidants and Mental Health
Antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, both linked to mental health issues.
Berries, citrus fruits, and leafy greens are rich in antioxidants and can help promote mental well-being.
Protein and Neurotransmitters
Amino acids from protein sources are essential for neurotransmitter synthesis, ensuring your brain has the resources it needs to function optimally.
Including protein-rich foods like lean meats, fish, and legumes in your diet can support mood regulation.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
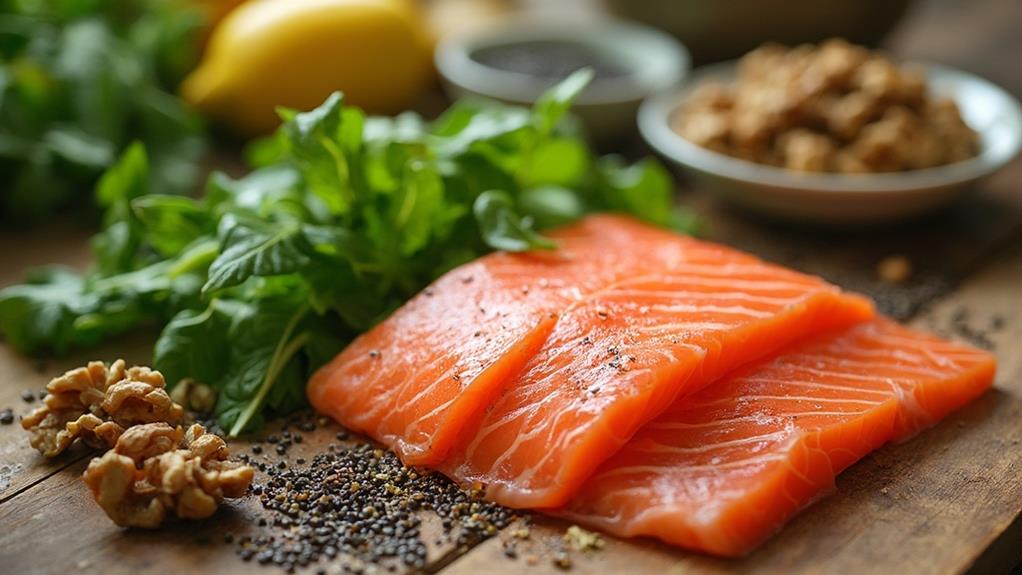

Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in enhancing mental health and emotional well-being. These essential fats, primarily found in fatty fish like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds, have been linked to reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Research suggests that omega-3s can influence neurotransmitter function, particularly serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for regulating mood.
Incorporating omega-3s into your diet can improve overall mood and cognitive function. Studies indicate that individuals who consume higher amounts of these fatty acids tend to experience fewer mood swings and lower levels of psychological distress.
This is especially important for those who may be struggling with mental health issues.
Omega-3s possess anti-inflammatory properties that contribute to brain health. Chronic inflammation has been associated with various mental health disorders, so ensuring an adequate intake of omega-3s might help mitigate these risks.
Effects of Processed Sugars
Reducing Processed Sugars Improves Mental Health
Cutting back on processed sugars can significantly benefit your mental health. High sugar intake is linked to mood swings, anxiety, and depression. This is because sugary foods cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, followed by a crash that leaves you feeling irritable and fatigued.
This rollercoaster effect can contribute to feelings of anxiety and exacerbate existing mental health issues.
Inflammation from Processed Sugars Affects Brain Health
Diets high in processed sugars are linked to inflammation, which is a factor in mental health disorders. Inflammation disrupts neurotransmitter function and leads to a decline in overall brain health, affecting your mood and cognitive abilities.
Stabilizing Blood Sugar Improves Energy and Mood
Consuming sugary snacks may provide a temporary energy boost, but this is often followed by a significant drop, leaving you craving more sugar.
Reducing processed sugar intake and opting for whole foods stabilizes blood sugar levels, leading to more consistent energy and improved mood. By making these dietary changes, you can take charge of your mental well-being and enhance your overall quality of life.
How Does Filipino Cuisine Affect Mental Health and Well-being Compared to Other Cultures?
The holistic approach to filipino health considers not just physical well-being, but also mental and emotional health. Filipino cuisine, rich in fresh ingredients and diverse flavors, contributes to a sense of comfort and connection, which can positively impact mental well-being. The communal aspect of Filipino dining also fosters a sense of belonging and emotional nourishment.
Foods That Enhance Cognitive Function

Foods That Enhance Cognitive Function
1. Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fatty fish support brain health and cognitive function. Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, found in fish like salmon and sardines, have been shown to lower the risk of dementia and improve cognitive function.
2. Blueberries: Packed with antioxidants, blueberries improve communication between brain cells and may delay brain aging. The antioxidants in blueberries, such as anthocyanins and flavonoids, have been found to enhance memory and cognitive function.
3. Turmeric: Turmeric contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that boost memory and stimulate new brain cell growth. Curcumin has been shown to cross the blood-brain barrier, reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain.
4. Leafy Greens: Leafy greens, such as kale, spinach, and broccoli, are high in vitamins and nutrients that support brain health and cognitive function. Vitamin K, found in these vegetables, plays a critical role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the maintenance of healthy neurons.
Incorporating these foods into your daily meals can provide the essential nutrients your brain needs to function at its best.
The Importance of Hydration
Hydration is essential for optimal brain function. Even mild dehydration can impair cognitive abilities and mood. When you're well-hydrated, your brain can perform at its best, helping you focus, think clearly, and manage stress effectively.
Dehydration can significantly impact mental health. The level of hydration directly affects emotional well-being. To understand this connection, consider the following effects of hydration levels on mental health:
| Hydration Level | Effects on Mental Health |
|---|---|
| Well-hydrated | Enhanced mood, better focus |
| Mildly dehydrated | Increased anxiety, fatigue |
| Severely dehydrated | Impaired cognition, irritability |
In essence, staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining a healthy brain and emotional state.
Mindful Eating Practices

Mindful eating practices can transform your relationship with food and its impact on mental health. By focusing on the present moment while you eat, you can cultivate a deeper awareness of your body's signals and emotions. This shift not only enhances your enjoyment of food but also fosters a healthier mindset.
To adopt mindful eating practices, follow these steps:
1. Slow Down Your Eating: Take your time with each meal. Chew your food thoroughly and savor the flavors, which can lead to better digestion and satisfaction. For example, try to chew each bite 20-30 times before swallowing.
2. Eliminate Distractions: Put away your phone and turn off the TV. Create an environment that encourages you to focus solely on your meal. This means eating in a quiet room or area without electronic devices.
3. Listen to Your Body's Hunger and Fullness Cues: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues. This awareness can help you avoid overeating and promote healthier choices. For instance, stop eating when you feel satisfied, rather than stuffed.
4. Appreciate Your Food: Consider where your food comes from and the effort that went into it. This appreciation can enhance your connection to what you eat. Think about the farmers who grew your vegetables, the cooks who prepared your meal, or the people who harvested your favorite ingredients.