Food and Filipino Health: A Holistic Approach
Food plays a vital role in Filipino health and well-being. It is deeply rooted in the culture, with staple foods like rice and local vegetables providing essential nutrients to the body.
Traditional dishes like sinigang and adobo offer both flavor and health benefits, as they are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients.
Communal dining is an integral part of Filipino culture, and it strengthens family bonds and fosters a sense of community. This, in turn, enhances mental wellness by providing emotional support and reducing stress.
Each meal reflects Filipino identity, evoking memories and reinforcing cultural values.
Sustainable food practices support both health and the environment. Sourcing local ingredients reduces carbon footprint and supports local farmers, while also providing fresh and nutritious food.
Understanding the multifaceted role of food in daily life can enrich experiences and connections with others, by promoting a sense of community and cultural heritage.
Traditional Filipino Ingredients
Traditional Filipino ingredients are the foundation of the country's diverse culinary landscape, deeply rooted in its history and culture.
Rice is a staple ingredient in Filipino cuisine, forming the foundation of many meals and symbolizing sustenance and community. Other essential vegetables like eggplant, bitter melon, and leafy greens provide vital vitamins and minerals that contribute to health and well-being.
The art of lechon roasting is a centuries-old practice that symbolizes celebration. This traditional dish brings together various ingredients to create a meal that's both delicious and culturally significant.
Filipino cuisine is known for its bold flavors and vibrant presentations, as seen in the Parada Ng Lechon festival, where over 1000 creatively dressed lechons are paraded, symbolizing prosperity and festivity.
Seafood and meats are significant ingredients in Filipino cuisine, often sourced from local markets. Ingredients like pork, chicken, and fish reflect the region's geography and farming practices, and aren't just protein sources.
Condiments like soy sauce, vinegar, and bagoong (fermented shrimp paste) add depth of flavor and nutritional value to many traditional dishes.
Herbs and spices like garlic, ginger, and lemongrass elevate flavors and offer health benefits, ranging from anti-inflammatory properties to digestive support.
Communal Dining Practices
Communal Dining: A Cherished Filipino Tradition
Gathering around the dining table is a vital part of Filipino culture, fostering strong family bonds and a sense of community. Sharing meals promotes social interaction, emotional well-being, and better mental health by reducing feelings of isolation and increasing a sense of belonging. This is supported by research, which highlights the importance of communal dining in maintaining overall well-being.
Filipino households often practice communal dining, where a variety of dishes are served on a large platter, encouraging everyone to share and interact. This practice promotes generosity, camaraderie, and a sense of togetherness.
Meals typically feature a range of dishes, reflecting the cultural emphasis on diversity and balance in nutrition.
Communal dining also fosters intergenerational relationships, allowing younger family members to learn from their elders and share stories and experiences. This nurturing environment not only enhances appreciation for food but also reinforces cultural values, making it an essential aspect of Filipino identity.
By embracing communal dining practices, individuals actively contribute to a tradition that uplifts both physical and mental health, leading to holistic well-being.
Cultural Significance of Meals
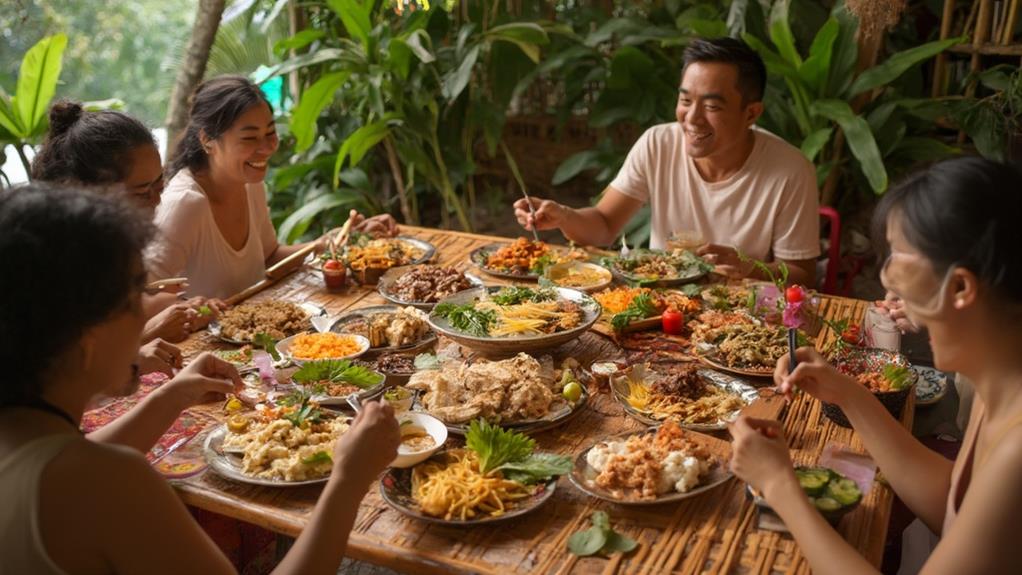

Meals hold profound cultural significance in Filipino society, acting as a medium for expressing identity and values. They represent more than just sustenance; they embody traditions, family ties, and community bonds. When you share a meal, you're participating in a rich tapestry of customs that have been passed down through generations.
Meals strengthen familial relationships. Sharing meals with family members creates opportunities for bonding and reinforces family ties. For example, Sunday family lunches are a common practice in many Filipino households, where families gather together to share a meal and catch up on each other's lives.
Food plays a key role in festivities. In Filipino culture, food is an essential component of celebrations. Lechon, a whole roasted pig, is often served during fiestas, symbolizing abundance and prosperity.
Ingredients and dishes reflect local culture. The use of specific ingredients and cooking techniques in certain regions of the Philippines reflects the unique cultural identity of that area. For instance, sinigang, a sour soup, is a popular dish in the southern region, showcasing the region's distinct flavor profile.
Sharing food signifies kindness and respect. In Filipino culture, offering food to guests is a sign of hospitality and respect. When visiting someone's home, it's customary to be offered snacks or refreshments, which symbolizes the host's warmth and welcoming nature.
How Can Traditional Filipino Food Contribute to Holistic Health and Well-being?
Traditional Filipino food holds the potential to contribute to holistic health and well-being. With future filipino food health research innovation, we can uncover the nutritional benefits of dishes like sinigang, adobo, and kare-kare. By embracing these traditional dishes, we can promote a healthier lifestyle rooted in cultural heritage.
Emotional Connections With Food
Food serves as a bridge between our past and present, forging deep emotional connections that resonate throughout our lives.
In many cultures, including Filipino, meals aren't just about sustenance; they're a vital aspect of social gatherings, family traditions, and celebrations. For instance, sharing a plate of adobo or sinigang creates memories tied to family gatherings or festive occasions.
The aroma of certain foods can evoke strong memories, often linked to specific flavors and aromas. Research has shown that smells can trigger powerful recollections. For many Filipinos, the scent of freshly cooked lumpia reminds them of their grandmother's kitchen, while the taste of leche flan transports them back to childhood birthdays.
These sensory experiences shape our emotional well-being, providing comfort and a sense of belonging.
Health Benefits of Local Dishes

Local dishes in the Philippines offer a wealth of health benefits. By incorporating fresh, local ingredients, these dishes often provide essential nutrients that support overall well-being.
Sinigang, made with tamarind and various vegetables, is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, which can boost your immune system and help fight inflammation.
Traditional cooking methods preserve the nutritional value of ingredients. Many traditional recipes use cooking methods like steaming and boiling, which help retain the nutrients in the food.
Adobo, a popular dish, typically features protein-rich meats marinated in vinegar and soy sauce, providing a source of iron and protein while also being lower in calories due to its lean preparation.
Local staples are high in fiber. Brown rice and root vegetables, such as sweet potatoes, are rich in fiber, which can improve digestion and help maintain a healthy weight.
The diverse use of herbs and spices, such as ginger and garlic, contributes to heart health and anti-inflammatory properties, enhancing flavor and providing additional health benefits.
Sustainable Food Practices
Embracing Sustainable Food Practices in the Philippines
Promoting Health and Environmental Well-being
Embracing sustainable food practices is crucial for promoting both health and environmental well-being in the Philippines. This can be achieved by making conscious choices that contribute to a healthier planet and community.
Adopting Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices not only reduce waste but also encourage the consumption of local, nutritious foods. The abaca industry's community engagement and sustainable practices can serve as a model for other industries.
Supporting local farmers and conserving natural habitats can provide valuable lessons for the food industry.
Practical Tips for Sustainable Food Practices
Choose Local Produce: Support local farmers and reduce carbon footprints by purchasing fresh fruits and vegetables from nearby markets.
Minimize Food Waste: Plan your meals and use leftovers creatively to avoid throwing away edible food.
Grow Your Own Food: Even small spaces can yield a variety of crops, providing fresh ingredients for your meals.
Practice Mindful Eating: Savor your meals, which can promote better digestion and reduce overeating.
Engage in Community Gardens: Engage with your neighbors in cultivating shared spaces, fostering community ties and healthy eating habits.